Be able to identify the country of origin and important facts about the following people, groups, and terms
* Fidel Castro
* Salvadore Allende
* Augusto Pinochet
* Jose Duarte
* Juan Peron
* Che Guevara
* Manuel Noriega
* Juan Alvarado
* Alejandro Toledo
*cooperative
* Shining Path
* PRI
* John F Kennedy
* Sandinistas
* Falkland Island conflict
* Violeta Barrios de Chamorro
Essay questions
* In what ways have Cuba's fortunes been influenced by the Soviet Union?
* What types of social problems have led to the recent move towards democratic governments in Latin American countries?
* What factors led to the PRI's loss of political power in Mexico?
* What types of policies have characterized the rule of Latin American military governments since 1945? Discuss specific examples
* What effects did foreign involvement in Latin America have on different countries? Did it make things bette or worse?
Agenda & Homework
10/2 - Read Ch 3 section 2 and take notes
Friday, May 6, 2016
Tuesday, April 26, 2016
Butter Battle Book Assignment
2. Answer the following questions
1.Why were the two groups at war?2. Why do you think they kept building bigger and bigger weapons?
3. How was the story like real life?
4. What was the purpose of the author?
5.How is the end of the book ambiguous?6.List reasons for war in general and the effects on all involved.
1.Why were the two groups at war?2. Why do you think they kept building bigger and bigger weapons?
3. How was the story like real life?
4. What was the purpose of the author?
5.How is the end of the book ambiguous?6.List reasons for war in general and the effects on all involved.
3. Choose one of the 3 options and complete
Option 1: Write an ending to the story. Your ending must be at least 2 paragraphs long and be in the style of Dr. Seuss (Rhyming)Option 2: Draw an ending to the story. Your ending must include a paragraph that explainsyour ending AND be colored.Option 3: Write a compare and contrast paragraph or essay about The Butter Battle Book story and the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1963.
Friday, April 15, 2016
Cold War Extra Credit
Cold War Trading Cards
Choose at least 5 of the events/people below. For each, create a trading card.
Each card should be no larger than a 3x5 index card.
On the front, you need a picture of the topic along with the name of the topic.
On the back, include the important statistics: Name, date, why it's important, what happened/what they did, important facts
All work should be neatly outlined (NO PENCIL!). Make it look as good & colorful as possible.
On a separate paper (or separate index card) include your sources.
*if you need ideas on what trading cards look like, google them!*
Possile topics:
Truman Doctrine
Marshall Plan
Division of Germany
Berlin Blockade
Berlin Wall
Cuban Missile Crisis
Bay of Pigs Invasion
Korean War
Vietnam War
Arms Race
Space Race
John F Kennedy
Nikita Kruschev
Winston CHurchill
Lyndon B Johnson
Choose at least 5 of the events/people below. For each, create a trading card.
Each card should be no larger than a 3x5 index card.
On the front, you need a picture of the topic along with the name of the topic.
On the back, include the important statistics: Name, date, why it's important, what happened/what they did, important facts
All work should be neatly outlined (NO PENCIL!). Make it look as good & colorful as possible.
On a separate paper (or separate index card) include your sources.
*if you need ideas on what trading cards look like, google them!*
Possile topics:
Truman Doctrine
Marshall Plan
Division of Germany
Berlin Blockade
Berlin Wall
Cuban Missile Crisis
Bay of Pigs Invasion
Korean War
Vietnam War
Arms Race
Space Race
John F Kennedy
Nikita Kruschev
Winston CHurchill
Lyndon B Johnson
Wednesday, April 13, 2016
Cold War Timeline
1945 - WWII ends
1945-1948 - Soviet controlled communist governments are set up in East Germany,Bulgaria,
Romania, Poland, and Hungary
1947 - Truman Doctrine & Marshall Plan put into action (see previous notes)
1948 - Germany divided into 4 zones
1949 - West & East Germany created
- China becomes Communist
- USSR develops atomic bomb (arms race begins)
-NATO formed
1950 - Korean War begins
1953 - Stalin dies, Khrushchev takes power
1955 - Warsaw Pact
1956 - "Destalinization" - Khrushchev's policy to get rid of Stalins more strict policies
- Uprisings in Poland, Hungary, and Czechoslovakia threaten Soviet power in Eastern
Europe
1957 - Space race gets more serious when the USSR is first to put a satellite in space
1959 - Fidel Castro takes over Cuba, sets up a Soviet supported dictatorship
1961 - construction begins on the Berlin Wall to stop East Germans from moving to West Berlin
1962 - Bay of Pigs Invasion - USA's plan to overthrow Castro fails miserably
- Cuban Missile Crisis - USSR puts missiles in Cuba, US blockade of Cuba almost leads to
nuclear conflict
1964 - US sends troops to Vietnam to help stop the spread of communism in Asia
1945-1948 - Soviet controlled communist governments are set up in East Germany,Bulgaria,
Romania, Poland, and Hungary
1947 - Truman Doctrine & Marshall Plan put into action (see previous notes)
1948 - Germany divided into 4 zones
1949 - West & East Germany created
- China becomes Communist
- USSR develops atomic bomb (arms race begins)
-NATO formed
1950 - Korean War begins
1953 - Stalin dies, Khrushchev takes power
1955 - Warsaw Pact
1956 - "Destalinization" - Khrushchev's policy to get rid of Stalins more strict policies
- Uprisings in Poland, Hungary, and Czechoslovakia threaten Soviet power in Eastern
Europe
1957 - Space race gets more serious when the USSR is first to put a satellite in space
1959 - Fidel Castro takes over Cuba, sets up a Soviet supported dictatorship
1961 - construction begins on the Berlin Wall to stop East Germans from moving to West Berlin
1962 - Bay of Pigs Invasion - USA's plan to overthrow Castro fails miserably
- Cuban Missile Crisis - USSR puts missiles in Cuba, US blockade of Cuba almost leads to
nuclear conflict
1964 - US sends troops to Vietnam to help stop the spread of communism in Asia
Tuesday, April 12, 2016
The Cold War Begins (12-1) part 2
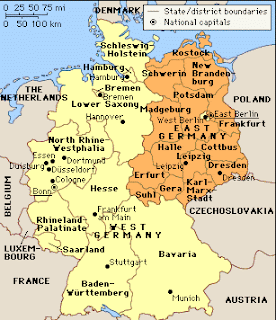
Germany after the division
Here's Berlin..and the Berlin Wall -

ORGANIZATIONS & ALLIANCES
NATO - (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) - 1949 -
-USA, Canada, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Holland, England, Italy, Denmark, Norway, Portugal, Iceland (West Germany, Turkey, & Greece join later)
-Agree to help one another if attacked
Warsaw Pact - 1955
-USSR, Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, and Romania
-agree to help one another if attacked
SEATO - (Southeast Asia Treaty Organization) early 1950's
-USA, England, France, Pakistan, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, New Zealand
- goal was to stop Soviet agression in the East
CENTO - (Central Treaty Organization)
- USA, England, Iraq, Iran, Turkey, Pakistan
-goal was to stop Soviet agression in the south
Cold War
What is the Cold War?
• It’s the period from 1946 to 1989 where the Soviet Union (Russia ) and the United States
• It’s a “cold” war because the 2 countries never actually fought each other, but they did help other countries fight
What was the problem?
• The US
• The Soviet Union is communist. That means that the government owns all the factories and the people can’t own their own business, and there are a limited number of products to buy.
• These two ideas are so opposite that each is threatened by the other.
• Capitalists think that communism takes away individual freedoms
• Communists think capitalism is excessive (too much stuff, to much control by individuals)
• So after WWII, both sides wanted the newly free countries of Eastern Europe to be like them.
• Soviet goal: spread communism, become a world power
• US/England goal: stop communism, keep Soviet Union from getting too powerful
The Beginning
• 1946 – civil war in Greece – Soviets support the Communists, England
• 1947 - TRUMAN DOCTRINE
• US policy that would give $$ to any country threatened by communism (like Greece
• Goal: to stop the spread of communism
– MARSHALL
• $13 billion to fix the European economy
• The idea was that if the economy is good, the country won’t want to be communist
• 1946-49: Division of Germany
– After the war, it was split into 4 parts; England , USA , France , and Soviet Union each got a part
• The capital, Berlin
– England , USA , and France combined theirs and re-named it the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany
– The Soviet Union named theirs the German Democratic Republic (East Germany
the problem?
• ¾ of Berlin was capitalist and democratic, while the other ¼ was communist, and it was right in the middle of communist East Germany
• The soviets decided to try and stop any goods from getting to West Berlin, so for a year, the US
• Another problem was that many people in East Germany West Berlin .
• 1949
– Arms Race: the US
• The problem was that if either side actually fired the weapons, both countries could be destroyed
– Creation of new alliances
• NATO (Europe, US, and Canada
• Warsaw
• CEATO & SENTO (central asia , middle east, & S.E. Asia)
• 1955 – after Stalin dies, Khrushchev takes over
• 1956 – countries in Eastern Europe (Hungary , Poland ) try to break away from the Soviet union , but the Soviet army invades and takes over
• 1959 – Fidel Castro takes over in Cuba
– He is a totalitarian dictator, and is supported by the Soviet Union
• 1950’s
• Korean War: North Korea (Communist) vs South Korea
– US sends troops in to fight with the South Koreans; China and USSR
• Space Race begins – US and Soviets try to be the first into space. The 1st satellite into space was the Soviet’s, the first man on the moon was the US
The Berlin
• After years of East Germans escaping to West Berlin, Khrushchev decides to set up a barrier to keep them out of West Berlin .
• The wall completely surrounds W. Berlin – the people inside are allowed to come out, but the people outside can’t come in.
• It’s guarded by guards, barbed wire, machine guns, attack dogs, and mines.
• 1960 - The US
• Khrushchev decides to use Cuba US
• 1962 - Cuban Missile Crisis –the US and Soviet Union almost start a war when they can’t agree on what should happen with Cuba
Vietnam War
• 1965 – President Johnson sends US soldiers into Vietnam
• He wanted to make sure that the communist North Vietnam wouldn’t take over south Vietnam US was worried that if Vietnam became communist, all of Asia would soon be as well
• This is called the Domino Theory.
• In 1973, the US
Sunday, March 20, 2016
WWII Extra Credit
Watch one of the following movies (or one approved by Ms. G.
Write a 1-2 page minimum essay that includes:
- a summary of the movies
- ways the movie was historically accurate
- ways the movie was inaccurate
List of films
Windtalkers
Band of Brothers (pick an episode)
Flags of Our Fathers
The Desert Fox
The Great Escape
Tora! Tora! Tora!
Enemy at the Gates
Monuments Men
Schindler's List
The Pianist
Stalingrad
Pearl Harbor
Defiance
Saving Private Ryan
The Thin Red Line
Memphis Belle
Write a 1-2 page minimum essay that includes:
- a summary of the movies
- ways the movie was historically accurate
- ways the movie was inaccurate
List of films
Windtalkers
Band of Brothers (pick an episode)
Flags of Our Fathers
The Desert Fox
The Great Escape
Tora! Tora! Tora!
Enemy at the Gates
Monuments Men
Schindler's List
The Pianist
Stalingrad
Pearl Harbor
Defiance
Saving Private Ryan
The Thin Red Line
Memphis Belle
Friday, March 18, 2016
11-2 New Order & the Holocaust
The New Order
By 1942 Germany controlled most of Europe
2 kinds of control:
Direct control = annexation
These areas, like Poland, became part of Germany
Occupation = German military (SS) + local supporters keep control over the area
Remember, Hitler's goal was to create a perfect Aryan state
He viewed many different types of people as inferior and unfit to be part of this empire.
This included the Slavic people, who lived in Poland, Croatia, Czechoslovakia, and the rest of Eastern Europe.
As Hitler took over, he moved these people from their land into concentration camps & farms to be used as slave labor
As Hitler took over, he moved these people from their land into concentration camps & farms to be used as slave labor
He moved Germans in to populate these areas
Other Groups Hitler didn’t feel were good enough to be in his Empire
Jews
Gypsies (Romany)
Slavic People
Jehovah’s Witnesses
Homosexuals
The Mentally Handicapped
Socialists
These are the groups that ended up in Nazi camps
Hitler, with many other Germans, blamed the democrats, the radicals, the communists, the liberals, and the Jews for Germany losing the war in 1918.
Those who signed the surrender papers and the Versailles Treaty and set up the Weimar Republic were traitors.
Hitler accused the Jews of trying to destroy his Aryan Nation
To remove the “threat” that the Jews posed, Hitler and his top officials came up with a plan that would later be known as the “Final Solution”
What was the final solution?
Genocide
It was not an overnight decision, but one that evolved slowly over time
Step 1: the Ghettos
In Poland, all Jewish people were taken from their homes and placed in specific areas of the city known as ghettos.
separated from the rest of the city by fences of barbed wire or walls
They were not allowed to leave exept to work (under supervision) and got very little supplies
Life in the Ghetto
People lived in cramped quarters
Many Jews died from starvation
diseases such as typhoid and tuberculosis lead to many deaths
Any Jew attempting to leave the ghetto was shot.
They began to give away their clothing in exchange for food.
To survive, the Jews resorted to smuggling food into the ghetto through the black market.
Step 2: Einsatzgruppen
The SS created the Einsatzgruppen, a special military unit that was responsible for following the army through Eastern Europe & Russia
They rounded up the Jews in each town together and shot them.
Step 3: The Camps
All over Eastern Europe and within Germany, the Nazis set up concentration camps, labor camps where the prisoners were used as workers in factories and performed other jobs.
Who was in these camps?
Political prisoners
P.O.W.s
Communists & socialists
All other targeted groups
In Poland, 6 special camps were set up.
These were death camps, specially made to kill people.
When the ghettos were emptied towards the end of the war, this is where the are sent
The camps:
Chelmno
Auschwitz II
Treblinka II
Majdanek
Belzec
Sobibor
The Death Toll
6 million Jews
40% of the Gypsy population in Europe (400,000)
4 million Eastern Europeans
3-4 million Russian prisoners of war (P.O.W.s)
Total: around 13 million people died in the concentration & death camps
Resistance
There were people that took a stand and fought back against the Nazis
In the ghettos, the people held uprisings
Most famous: Warsaw Ghetto Uprising
The largest single revolt during the war
The people in the Warsaw ghetto held off soldiers for almost a month in 1943 when the Nazis were trying to ship them all off to Treblinka
Resistance fighters who fought back against the Nazis throughout Russia, Poland, Italy, France, and Eastern Europe
They used guerrilla tactics
Lived in the woods
Attacked rail cars, shipping convoys, destroyed railroad tracks
Mussolini was killed by partisans
Some people hid Jews from the Nazis
Others helped them escape to other countries
New Order in Japan
Japan took over Southeast Asia and created the Greater East Asian Co-Prosperity Sphere
They put the military in charge in every country they took over
The native people were treated very badly
Forced to work for the Japanese
Their food was given to the soldiers so they starved
Their traditions were ignored
Many died
Kids in WWII
In England, when the bombing started, a lot of kids were sent to the US
In Germany & England, many kids were sent to the countryside to avoid the bombing of cities
In the camps, children were the first killed
Many kids became soldiers, as young as 13
By 1942 Germany controlled most of Europe
2 kinds of control:
Direct control = annexation
These areas, like Poland, became part of Germany
Occupation = German military (SS) + local supporters keep control over the area
Remember, Hitler's goal was to create a perfect Aryan state
He viewed many different types of people as inferior and unfit to be part of this empire.
This included the Slavic people, who lived in Poland, Croatia, Czechoslovakia, and the rest of Eastern Europe.
As Hitler took over, he moved these people from their land into concentration camps & farms to be used as slave labor
As Hitler took over, he moved these people from their land into concentration camps & farms to be used as slave labor
He moved Germans in to populate these areas
Other Groups Hitler didn’t feel were good enough to be in his Empire
Jews
Gypsies (Romany)
Slavic People
Jehovah’s Witnesses
Homosexuals
The Mentally Handicapped
Socialists
These are the groups that ended up in Nazi camps
Hitler, with many other Germans, blamed the democrats, the radicals, the communists, the liberals, and the Jews for Germany losing the war in 1918.
Those who signed the surrender papers and the Versailles Treaty and set up the Weimar Republic were traitors.
Hitler accused the Jews of trying to destroy his Aryan Nation
To remove the “threat” that the Jews posed, Hitler and his top officials came up with a plan that would later be known as the “Final Solution”
What was the final solution?
Genocide
It was not an overnight decision, but one that evolved slowly over time
Step 1: the Ghettos
In Poland, all Jewish people were taken from their homes and placed in specific areas of the city known as ghettos.
separated from the rest of the city by fences of barbed wire or walls
They were not allowed to leave exept to work (under supervision) and got very little supplies
Life in the Ghetto
People lived in cramped quarters
Many Jews died from starvation
diseases such as typhoid and tuberculosis lead to many deaths
Any Jew attempting to leave the ghetto was shot.
They began to give away their clothing in exchange for food.
To survive, the Jews resorted to smuggling food into the ghetto through the black market.
Step 2: Einsatzgruppen
The SS created the Einsatzgruppen, a special military unit that was responsible for following the army through Eastern Europe & Russia
They rounded up the Jews in each town together and shot them.
Step 3: The Camps
All over Eastern Europe and within Germany, the Nazis set up concentration camps, labor camps where the prisoners were used as workers in factories and performed other jobs.
Who was in these camps?
Political prisoners
P.O.W.s
Communists & socialists
All other targeted groups
In Poland, 6 special camps were set up.
These were death camps, specially made to kill people.
When the ghettos were emptied towards the end of the war, this is where the are sent
The camps:
Chelmno
Auschwitz II
Treblinka II
Majdanek
Belzec
Sobibor
The Death Toll
6 million Jews
40% of the Gypsy population in Europe (400,000)
4 million Eastern Europeans
3-4 million Russian prisoners of war (P.O.W.s)
Total: around 13 million people died in the concentration & death camps
Resistance
There were people that took a stand and fought back against the Nazis
In the ghettos, the people held uprisings
Most famous: Warsaw Ghetto Uprising
The largest single revolt during the war
The people in the Warsaw ghetto held off soldiers for almost a month in 1943 when the Nazis were trying to ship them all off to Treblinka
Resistance fighters who fought back against the Nazis throughout Russia, Poland, Italy, France, and Eastern Europe
They used guerrilla tactics
Lived in the woods
Attacked rail cars, shipping convoys, destroyed railroad tracks
Mussolini was killed by partisans
Some people hid Jews from the Nazis
Others helped them escape to other countries
New Order in Japan
Japan took over Southeast Asia and created the Greater East Asian Co-Prosperity Sphere
They put the military in charge in every country they took over
The native people were treated very badly
Forced to work for the Japanese
Their food was given to the soldiers so they starved
Their traditions were ignored
Many died
Kids in WWII
In England, when the bombing started, a lot of kids were sent to the US
In Germany & England, many kids were sent to the countryside to avoid the bombing of cities
In the camps, children were the first killed
Many kids became soldiers, as young as 13
Thursday, March 17, 2016
World War II timeline
1939
• SEPTEMBER
– 1st: Germany invades Poland
– 3rd: England &France
– 17: Russia invades Poland
– 28: Stalin&Hitler split Poland
• NOVEMBER
– 30th: USSR invades Finland
• PHONY WAR (9/39-4/40)
– Besides the invasion of Poland
Blitzkrieg
– “Lightning War”
– Germany
– Used to invade & conquer countries quickly using speed and surprise
– Tanks, in columns, supported by mobile infantry and air units
– Armored columns called Panzer divisions rolled in; dive bombers and other planes provided support
1940
• APRIL
– Germany invades Denmark and Norway
• MAY
– Blitzkrieg used against Poland , Belgium , and France
• WESTERN OFFENSIVE
– Maginot Line
– Dunkirk
• JUNE
– Mussolini declares war on the Allies
– France signs cease fire with Germany
• Vichy France vs Free France
• JULY
– US stops shipment of materials to Japan
– Battle of Britain
• Luftwaffe attacks, Britain
• Battle of Britain
– Germany
– When that didn’t work, they switched to cities, hoping that the people would get defeated.
– This gave the British time to rebuild their air force, which allowed them to attack Germany
• AUGUST
– Italy invades Somalia
• SEPTEMBER
– Italy invades Egypt
– Germany , Italy , and Japan
• OCTOBER
– Italy invades Greece
• NOVEMBER
– British air force bombs Hamburg
1941
• MARCH
– Bulgaria
– Britain
– Desert War begins
• Erwin Rommel (“Desert Fox”)
• APRIL
– Germany , Italy and Bulgaria invade Yugoslavia
– Japan signs non-aggression pact with Russia
• JUNE
– Allies invade Syria
– Finland & Hungary declare war on USSR
– Operation Barbarossa
• JULY
– USSR & England sign mutual assistance treaty (against Germany
• DECEMBER
– Britain declares war on Finland , Hungary , and Romania
– Pearl Harbor
• December 7, 1941
• Japan attacks US fleet in Hawaii
• Kamikaze pilots are used
• At the same time, Japan invades Lalaya , Thailand , Philippines , & Burma
• The spark that causes the US to declare war on Japan
•
• Operation Barbarossa
• 3 million German soldiers and tanks were sent into Russia
• Violates the Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression Pact
• Beginning of the Eastern Front Conflict
• Sends Stalin to the Allies
1942
• FEBRUARY
– US sets up internment camps for Japanese Americans
– Japan takes control of Singapore and bombs Australia
• APRIL
– US bombs Tokyo
– Luftwaffe begins 2nd bombing of Britain
• MAY
– Battle of Coral Sea (US vs Japan
• JUNE
– Battle of Midway (US vs Japan
• Turning point of the war in the Pacific
• AUGUST
– 1st use of the Navajo code
• OCTOBER
– Battle of El Alamein
• NOVEMBER
– Battle of Stalingrad (11/42 – 2/43)
• Ends German hope of conquering USSR
• Turning point of the war in Europe
• FALL
– US
1943
• JANUARY
– Allies take Tripoli
• FEBRUARY
– Allies begin bombing Germany
• JULY
– Allies invade Sicily
– Italy
• Mussolini jailed, Victor Emmanuel becomes king again
• Italy
• NOVEMBER
– TEHRAN
• Meeting of Stalin, Roosevelt, and Churchill to plan the Final attack on Germany
• British start bombing of Berlin
1944
• Germany sends the army in to retake Italy Rome
• JUNE
– The allies free Rome
– D-DAY (Invasion of Normandy
• June 6
• JULY
– The Red Army pushes the Germans back through Russia
• AUGUST
– US army frees Paris
• SEPTEMBER
– Allies enter Germany
• OCTOBER
– Churchill, Stalin, and Roosevelt meet in Moscow
1945
• FEBRUARY
– Churchill, Stalin, and Roosevelt meet at Yalta
– Bombing of Dresden
– Battle of Iwo Jima
• APRIL
– Roosevelt dies and Harry S. Truman becomes the next president
– Mussolini is executed by Italian Partisans
– German forces in Italy
– Hitler Commits suicide
• MAY
– German troops in Czech, Holland , & Denmark
– 5/7 Germany
• End of the war in Europe
• AUGUST
– 8/6 US drops atomic bomb on Hiroshima
– 8/8 Russia declares war on Japan and invades Manchuria
– 8/9 US drops bomb on Nagasaki
– 8/14 Japan
Tuesday, February 16, 2016
11-1 Paths to War
11-1 Paths to War
HITLER BEGINS HIS CONQUEST OF EUROPE
Remember, Hitler’s goal was to create an Aryan empire, and he needed land to do this.
Remember, Hitler’s goal was to create an Aryan empire, and he needed land to do this.
• He planned to go to war with the USSR
STEP ONE
• Rebuilding the military:
– Creates new air force
– drafts people into the army
• 1936 – invasion of Rhineland
– Demilitarized zone between France and Germany
• No one stops Hitler’s advance. Why?
– They believe in appeasement
• Churchill is the leader of the move towards appeasement
HITLER'S FRIENDS
• Mussolini was working in his own empire. He invaded Ethopia
• H&M helped Franco win a war in Spain
• Rome-Berlin Axis= pact between Italy and Germany
• Anti-Comintern Pact = Japan and Germany
STEP TWO
• 1937- Anschluss
– Germany
– Austrian government allows Nazis to be put in charge of the gov’t.
– The new gov’t lets the Germans in
– Germany takes control of Austria
STEP THREE
• Hitler wanted to take over the Sudetenland , an area of Czech that was mostly inhabited by Germans
• He demands that it be given to him
• Munich
• They decide to give him the land
STEP FOUR
• The appeasement policy lads Hitler to believe that France and England
• He takes over the rest of Czechoslovakia (Bohemia
STEP FIVE
• Hitler demands part of Poland
• England and France
STEP SIX
• Hitler realizes that E&F are in talks with Stalin, and decides to get to him first to prevent another 2 front war
• Nazi-Soviet Nonagression pact (1939)
– In return for not attacking Germany , Russia would get the Baltic states and part of Poland
– He could make this promise because he planned to taking over USSR
STEP SEVEN: The Final Step
• Now confident that no one can defeat him, Hitler takes the step that leads to war
• September 1, 1939 – Hitler’s troops invade Poland
• 2 days later, England and France declare war on Germany
• Remember, Japan had taken Manchuria , been forced to give it back, then retaken by the new militant Japanese gov’t
– It was renamed Manchuko
– This made the US
WAR WITH CHINA
• Chiang Kai-Shek, the leader of China , had avoided worring about the threat of Japan
• By 1937, he had to be concerned as the Japanese army kept taking territory
• Eventually there was fighting, and Japan got a good chunk of eastern China
NEW ASIAN ORDER
• Japan ’s plan was to create a united Asian empire that it would control, and add parts of Russia
– It was counting on Hitler’s support
• After Hitler and Stalin signed their agreement, Japan
– Moved the focus to Southeast Asia , which had lots of natural resources
PROBLEMS ARISE
• When Japan takes control of French Indochina, the US
– Restrictions on trade
• This poses a problem, because Japan needs the resources that the US provides, but it also needs the materials from Asia
• The solution? Surprise attack on US and European colonies in SE Asia
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)